Eczema Skincare: Expert Strategies for Soothing and Managing Flare-Ups
Eczema (commonly called atopic dermatitis) is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by a compromised skin barrier, episodic flare-ups, and intense itch that disrupts sleep and daily life. This guide explains why flare-ups occur, how to identify and avoid triggers, what a gentle daily eczema skincare routine looks like, quick strategies to calm flares, and clear signs for when specialist care is needed. You will learn practical steps—rooted in barrier repair, anti-inflammatory choices, and environmental control—to stop itching fast and reduce flare frequency over time. The article covers trigger identification, a step-by-step routine (cleanse, moisturize, protect), immediate self-care and over-the-counter options, and red flags that warrant dermatology evaluation. Keywords such as sensitive skin eczema, atopic dermatitis, ceramides for eczema, and how to stop eczema itching fast are woven into actionable advice. Recent research indicates barrier-focused therapy and avoidance of common irritants remain central to managing chronic atopic dermatitis, and this piece shows how to apply those principles at home.
What Causes Eczema Flare-Ups and How Can You Identify Triggers?
Eczema flare-ups arise from an interaction between intrinsic factors (genetic predisposition and immune dysregulation) and extrinsic triggers (allergens, irritants, climate, and stress), which together impair the stratum corneum and amplify inflammation. Recognizing these drivers helps target prevention and immediate care because removing a trigger reduces immune activation and speeds barrier recovery. Common triggers are identifiable and often modifiable through product swaps, environmental controls, and behavioral changes that restore epidermal lipids and natural moisturizing factors. Keeping a brief symptom-and-exposure diary for several weeks reveals temporal patterns and helps prioritize which suspects to eliminate first. If triggers remain unclear or severe despite home adjustments, dermatologic evaluation can identify contact allergens or recommend patch testing to guide targeted avoidance and treatment.
Which Common Allergens and Irritants Trigger Eczema?

Common offenders include fragranced skincare products, preservatives, certain metals like nickel, and harsh detergents that strip epidermal lipids and destabilize the skin barrier. Clothing materials such as wool and rough synthetics can create friction and micro-trauma, while laundry residues and fragranced fabric softeners leave irritant residues that perpetuate itch and inflammation. Reducing exposure by choosing fragrance-free formulas, switching to soft cotton sheets, and using a gentle, enzyme-free laundry detergent lowers flare risk. Tracking exposure timing in a diary often links specific products or garments to symptom onset and allows stepwise elimination to confirm the cause.
How Do Stress and Environmental Factors Affect Eczema Symptoms?
Stress amplifies eczema via neuroimmune pathways—psychological stress increases cortisol and neuropeptide signaling, which can intensify itch and inflammatory cascades in atopic dermatitis. Environmental factors such as low humidity, cold air, and excessive heat or sweating further dry the stratum corneum and weaken barrier lipids, increasing transepidermal water loss and susceptibility to irritants. Practical controls include maintaining indoor humidity with a humidifier in dry months, avoiding very hot showers, and choosing breathable, layered clothing to reduce sweat-induced flares. Incorporating stress-reduction practices like brief breathing exercises and consistent sleep schedules helps break the itch-scratch cycle and supports long-term control.
Common environmental and lifestyle adjustments to reduce flares:
- Maintain humidity: Use a humidifier in dry climates to prevent skin drying.
- Adjust bathing habits: Take lukewarm, short showers and pat skin dry.
- Manage stress: Use daily relaxation techniques to lower neuroimmune triggers.
These practical steps create a foundation for daily skincare and immediate flare management described next.
What Is the Best Daily Skincare Routine for Sensitive Eczema-Prone Skin?
A daily eczema-friendly regimen focuses on gentle cleansing, consistent barrier repair with moisturizers, and protective measures against irritants and sun exposure to sustain epidermal lipids and reduce flares. Start with a mild, fragrance-free cleanser applied with lukewarm water for short intervals to minimize surfactant exposure, then apply an emollient to damp skin within three minutes to lock in moisture. Regular use of ceramide-containing moisturizers supports barrier reconstruction while humectants like glycerin or hyaluronic acid draw moisture into the epidermis; occlusives such as petrolatum can be used at night or on very dry patches. For those who need personalized product selection or prescription alternatives, a clinic consultation can help match formulation textures and active ingredients to individual skin severity and lifestyle.
How to Choose and Use Eczema-Friendly Cleansers and Moisturizers?
Selecting products requires looking for fragrance-free, low-pH cleansers with mild surfactants and moisturizers that contain ceramides, glycerin, or petrolatum depending on severity. Choose creams or lotions for daytime use when you need faster absorption and ointments for overnight repair on areas with deep fissuring or persistent dryness. Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing to trap water in the epidermis and reapply after handwashing or any activity that reduces skin hydration. Consistent, twice-daily maintenance plus targeted spot treatment prevents barrier decline and reduces the need for frequent anti-inflammatory prescriptions.
| Product Type | Key Ingredient & Texture | Recommended Use/Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cream | Ceramides, glycerin; semi-thick | Daytime maintenance for moderate dryness and active lifestyles |
| Ointment | Petrolatum; thick, occlusive | Overnight or on very dry, cracked areas to seal moisture |
| Lotion | Light emollients; low viscosity | Mild dryness, easier layering under clothing or makeup |
This table clarifies when to choose each texture to support barrier repair and daily function.
Which Key Ingredients Like Ceramides and Hyaluronic Acid Help Repair Skin Barrier?
Ceramides are lipid components of the stratum corneum that restore intercellular lamellae and reduce transepidermal water loss, directly improving barrier function and lowering inflammation. Humectants such as glycerin and hyaluronic acid attract and retain water in the epidermis, enhancing flexibility and making occlusive layers more effective when paired together. Combining humectants with occlusives is a knowledge-graph style solution: humectant → retains water → occlusive seals water → barrier restoration. Recent studies and clinical guidance emphasize ceramide-rich formulations as foundational therapy for sensitive skin eczema and atopic dermatitis management.
How Can You Soothe Eczema Flare-Ups Quickly and Effectively?
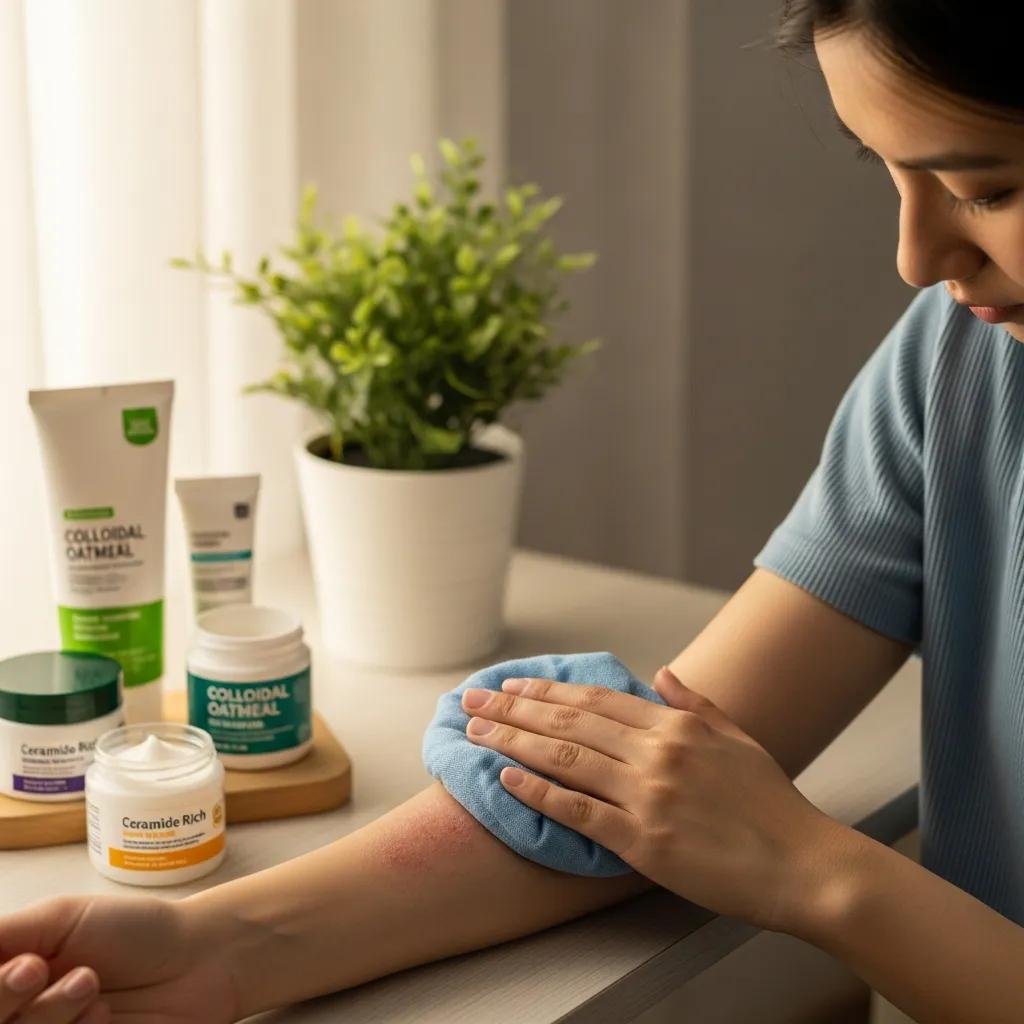

Immediate flare relief hinges on rapid barrier support, itch control, and infection surveillance to prevent complications; the prioritized approach is emollient application, symptom-directed OTC therapy, and escalation when needed. Cold compresses and wet-wrap therapy reduce itch and allow topical agents to penetrate, while prompt application of gentle emollients restores lipids and calms skin reactivity. Over-the-counter 1% hydrocortisone can reduce inflammation for short durations in limited areas; persistent, widespread, or recurrent flares require prescription-strength interventions under specialist supervision. Watch for signs of bacterial or viral infection—such as accelerating redness, pustules, or fever—and seek care promptly to avoid complications.
Immediate steps to calm a flare:
- Cool compresses: Apply for 10–15 minutes to reduce itch and inflammation.
- Moisturize liberally: Use an occlusive or thick cream to restore barrier lipids.
- Short-term 1% hydrocortisone: Apply to small, inflamed areas per package directions, then reassess.
These measures prioritize safety and rapid symptom control while monitoring for escalation indicators.
| Treatment | OTC vs Prescription, Onset | Use Case / Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Emollient application | OTC, immediate | Safe for all ages; foundational flare management |
| 1% Hydrocortisone | OTC, onset hours | Short-term use on limited areas; not for widespread severe flares |
| Topical steroid (prescription) | Prescription, rapid | Used for moderate-severe flares under supervision; potency and duration must be managed |
This table helps choose an appropriate next step during acute symptoms and clarifies when escalation is likely necessary.
What Are the Recommended Topical Treatments for Itch and Inflammation?
For mild localized flares, OTC 1% hydrocortisone can temporarily reduce itch and redness when used as directed and for short courses, but overuse risks skin thinning and tachyphylaxis. Prescription topical steroids and calcineurin inhibitors are more potent options tailored by severity, location, and patient age; these require medical oversight to select potency and duration safely. Non-steroidal topical agents and barrier-repair creams are adjuncts that reduce relapses when used consistently. If a flare fails to respond to judicious topical therapy or worsens, systemic evaluation and advanced options may be discussed with a dermatologist.
Which Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments Provide Flare-Up Relief?
Evidence-backed home strategies include colloidal oatmeal baths to soothe itch, regular emollient use to restore barrier lipids, and wet-wrap therapy for severe localized flares to enhance topical absorption and reduce scratching. Avoid unproven or harsh home procedures—such as concentrated bleach baths without guidance—because they can damage skin and increase sensitivity. Clothing choices that favor breathable, soft fabrics and avoidance of known irritants in cleaning products reduce daily skin stressors. Combining these practical measures with stress management and sleep hygiene decreases flare frequency over time.
When Should You Consult a Dermatologist for Eczema Management?
You should seek dermatology care when flares are severe, widespread, impair sleep or quality of life, fail to respond to appropriate OTC regimens, or when signs of infection appear; these red flags require specialist assessment and possible prescription therapy. A dermatologist will perform a focused history and skin exam, consider patch testing for contact allergens, evaluate for secondary infection, and design a stepped treatment plan that may include topical prescription agents or referral for systemic therapies when indicated. In practice, early specialist involvement benefits individuals with recurrent or treatment-resistant atopic dermatitis to reduce long-term morbidity and tailor maintenance strategies.
Red-flag signs to see a dermatologist:
- Widespread or rapidly worsening rash that limits daily function.
- Signs of infection such as pus, increasing pain, or fever.
- Failure of OTC measures after consistent application and optimization.
This checklist clarifies when home care is insufficient and specialty input can change outcomes.
What Personalized Treatments Does Shore MedSpa Offer for Eczema?
Shore MedSpa & Bio Aesthetics provides personalized evaluation by a board-certified dermatologist to assess persistent or severe eczema and recommend individualized treatment plans based on clinical findings. In Rockville, MD, the practice offers in-office assessment and physician-directed regimens that may include prescription topical therapies, guidance on advanced medical-grade options, and monitoring strategies tailored to each patient’s disease pattern. These assessments prioritize identifying triggers and optimizing barrier repair while minimizing unnecessary exposure to high-potency agents. For patients whose flares are uncontrolled with OTC care, a targeted dermatology visit often clarifies next steps.
How Does a Board-Certified Dermatologist Tailor Eczema Care Plans?
A dermatologist structures care by taking a detailed history of flare patterns, prior treatments, and possible triggers, then performing a skin exam to grade severity and check for infection or atopic comorbidities. Treatment choices follow a stepped approach: optimize emollients and trigger avoidance, add topical anti-inflammatories as needed, and escalate to systemic or procedural options only when indicated by disease severity or impact. Follow-up assesses response and adjusts potency, frequency, and adjunct measures such as patch testing or phototherapy referral when appropriate. This individualized workflow—assessment → targeted treatment → monitoring—ensures therapy matches both medical need and lifestyle considerations.